A Comprehensive Guide to Generative Engine Optimization
According to a 2025 study by Future Publishing, 27% of Americans now use AI large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT instead of traditional search engines.
And this number is likely to increase. One study found that the use of LLMs grew 80% over 12 months.
In fact, according to Semrush, the amount of traffic websites get from AI search will exceed that from search engines by 2028.
Traditionally, businesses have used search engine optimization (SEO) to attract users looking for information, products, and services online.
But things are changing. Businesses that only focus on SEO will lose out to those who also prioritize optimizing for AI, known as generative engine optimization (GEO).
So does this mean SEOs need to start again completely?
Well…no.
You see, not only does GEO have many of the same requirements as SEO, but the latter will continue playing a critical role in helping businesses gain visibility online.
This article explains what GEO is and how it works. We’ll also explain how you can adapt your SEO strategies to attract AI traffic.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization?
GEO is when you optimize your website for searches performed using chatbots or LLMs, instead of search engines.
The platforms it targets include:
ChatGPT
Google Gemini
Claude
Perplexity
It’s an evolution of SEO, which involves using techniques to appear in search results on platforms like Google. The higher your website appears in these search engine results pages (SERPs), the more clicks your website is likely to generate.
To understand how GEO and SEO work, it helps to understand how AI and traditional search work.
In a nutshell, the traditional search process involves:
The search engine visits websites and examines their content. This is known as “crawling”.
It then adds the content to its index. Search engines can only show indexed content.
When a user types a query, the search platform uses an algorithm to choose which indexed content to show the user.
It shows the user a list of ranked results that it thinks answers their question.
Traditional search engines also often show several sponsored results above the ranking articles. Appearing here is usually referred to as position “zero”; these companies have paid to be featured in this space.
For example, if we search “learn to code Python” on Google, we see a lot of sponsored results:
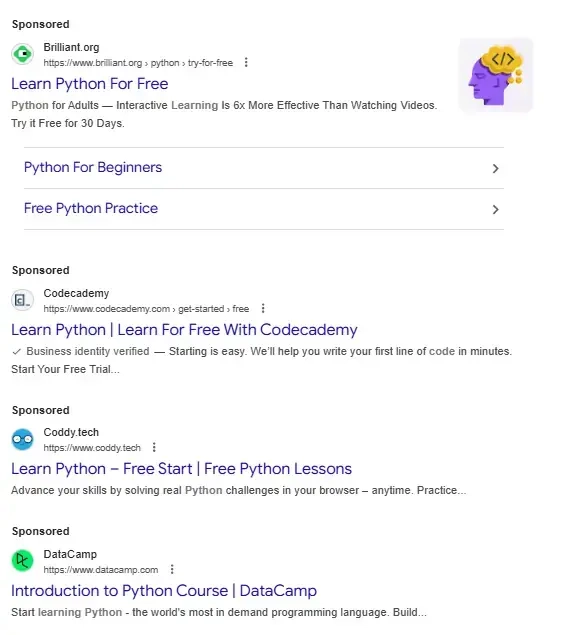
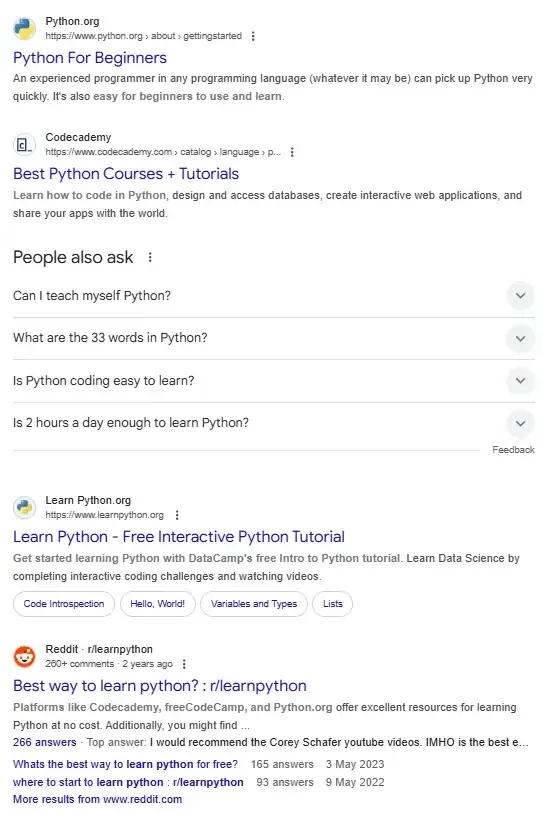
This is followed by the top organic results (those that Google isn’t paid to show you) and the “People Also Ask” section of related questions:
Generative AI search engines work slightly differently:
The user types a query.
The AI breaks down your query into multiple similarly targeted queries.
It sends these queries to a search engine.
It scans the top results, cross-references sources, and decides what information to ingest.
It then summarizes its findings; this often includes citations and links to sources.
Users then have the option to delve deeper by asking additional questions or refining the information provided by the platform.
Below is a response to the same query from ChatGPT. It begins by providing step-by-step instructions, with links to useful resources.
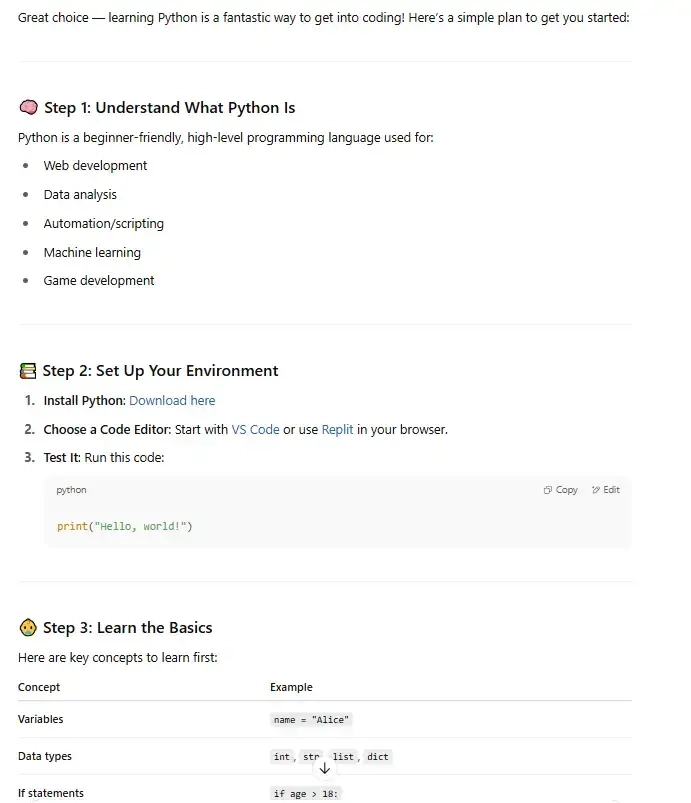
And then it suggests follow-up tasks:
This provides a more natural user experience and is easier than reading through search results to find the best source.
Search engine developers are aware of this and have begun integrating AI into their search results. These are known as AI overviews.
Google’s AI overviews now appear above search sponsored and organic search results. Here’s what it looks like for “learn to code Python”:

As you can see, it’s very similar to the response given by ChatGPT, providing step-by-step instructions and links to resources.
In some areas, Google has now rolled out “AI Mode”. This allows people to ask AI overviews follow-up questions.
Put simply, the line between LLMs and traditional search is becoming increasingly blurred, with traditional lists of search results giving way to more detailed, focused responses that directly address the user’s query.
What Does This Mean For SEO?
GEO isn’t replacing SEO. Instead, it’s adding an extra dimension, which means you need to consider where your page ranks and how the information on the page will be interpreted by LLMs.
Let’s take a deeper look at the impacts GEO will have on SEO.
Traditional search rankings still matter
As you can see, the AI doesn’t search the web itself. Instead, it uses a search engine just like in traditional search.
Where AI comes into play is the next stage: Comparing and analyzing results. In other words, users don’t need to worry about trawling through results trying to find the best and most relevant source.
This means that all of the techniques used in SEO still apply to GEO. However, you also need to consider new strategies that make your website and content easier for LLMs to scan and summarize; we’ll explain more about these later in the article.
Visibility will be harder to achieve
Generative search can make it harder to get online visibility. With search engines, ranking in the top ten ensures users at least see your brand, even if they don’t click on it.
With AI-driven search engines, unless the LLM uses your page as a reference, you won’t appear. Even if it is used, AIs often don’t display sources clearly to users, so they might not know the information comes from you.
GEO optimization involves ensuring your content is referenced, cited, or summarized by AI.
Bottom-of-the-funnel content is more likely to get engagement
SEO has traditionally used informational content to attract top-of-the-funnel (ToFu) traffic.
Some good examples of this include:
How to manage remote teams
Causes of chronic back pain
How to make cold brew at home
However, AI now essentially bypasses the need for users to read this kind of content and provides a better experience by allowing them to ask questions.
Bottom-of-the-funnel (BoFu) content, or searches where people want to buy something, are typically more likely to lead to clicks, as users often want to compare or research options themselves.
Examples of these kinds of search terms might be:
Best remote team management software
Chiropractor near me
Buy cold brew coffee
This means that SEO strategies may become more focused on BoFu searches, while GEO targets ToFu content.
GEO probably won’t change local search (for now)
While generative AI is shaking up how people find information online, local search remains a different beast entirely, and it's unlikely to be disrupted by GEO in the immediate future.
That’s because local search results are heavily tied to information pulled from Google Business Profiles, including:
Google’s local pack and map listings
User proximity
Reviews, business hours, and location-based data
When someone searches for “coffee shop near me” or “emergency plumber in Bristol,” they’re not looking for an AI-generated answer; they want nearby options, fast. And Google’s already incredibly good at surfacing those with maps, directions, and phone numbers.
Businesses that target these kinds of searches probably don’t need to worry about optimizing for GEO. However, the situation is rapidly changing, and new technologies could provide a better service than Google.
6 Generative Engine Optimization Tips
GEO essentially involves doing everything you normally would for SEO, but making your content and website easier for AI to access, understand, and use in its responses.
Let’s take a look at how to adapt our traditional SEO practices to account for GEO. As usual, the place to start is with keyword research.
1. Broaden your keyword strategy
At its core, keyword research is about understanding what your audience is searching for, how they’re phrasing those questions, and what kind of content they expect to find.
That’s still the foundation of any good SEO strategy, whether you’re trying to rank on Google’s first page or show up in an AI-generated answer.
However, the way AI-powered search engines use keywords does make some factors more important than before. They are:
User intent and depth help AI create detailed responses
A keyword with moderate volume but high informational value might be more likely to trigger an AI summary than a broad, high-competition term. That’s because AI models want information that they can use in detailed responses that directly match the user’s query.
Clusters and context matter more
Remember how earlier we mentioned that generative AI breaks your query down into multiple similarly targeted queries? This means that instead of focusing on single high-volume terms, SEOs now need to target topic clusters. This is when a primary keyword is supported by related terms and follow-up questions.
A good example of a topic cluster might be retro gaming. Create a pillar page that covers the complete history of gaming, listing every console from the Magnavox Odyssey through to the PlayStation 4, as well as key events such as the North American video game crash of the early 1980s.
This would link to more detailed articles on these related subjects.
Covering the topic in detail in this way makes it more likely that LLMs will find one of your pages in their multiple targeted queries, which in turn increases the likelihood that your content will be surfaced in the response.
Question-based keywords are more common in AI search
Phrases like “how does link building improve SEO?” or “best tools for earning backlinks” closely match the types of questions generative engines are designed to answer. Creating content around these queries increases the chances that your page will be selected, summarized, or referenced in an AI-generated response.
💡Pro tip
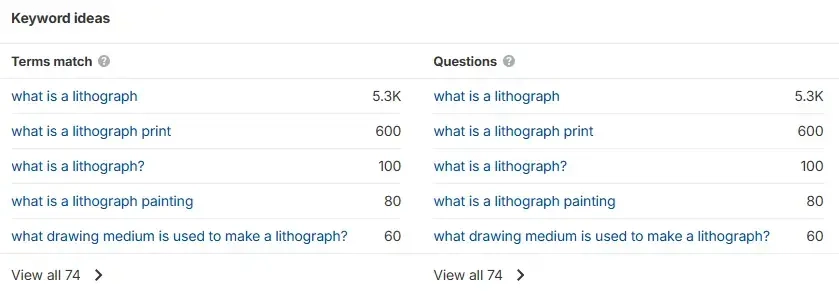
SEO tools are useful for identifying topic clusters and finding question-based keywords.
For example, type a term into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer and you’ll be shown a range of keyword ideas. This includes questions and other keywords that include the same terms.
2. Make your content GEO-friendly
One of the best things you can do to ensure you show up in AI searches is to present your content so it’s easy for AI to understand and serve in its responses.
There are a ton of ways to do this. Let’s take a look at each.
Answer questions clearly
Ensure your content answers people’s questions clearly, quickly, and in the way users expect. For example, if readers want to know the best CRM for IT sales, don’t begin with a long explanation of why CRMs are important in IT.
Get to the point by opening with something like: “Overall, the best CRM for IT companies is X. Here’s a quick overview of nine other options.”
Generative engines like Google’s AI Overviews or ChatGPT might use keywords to find mentions. But when it comes to choosing which to use, they look for complete, coherent answers.
Here’s how to answer user questions clearly:
Using questions as headings makes it easy for AI tools to identify each section’s purpose.
Lead with the answer, as described above.
Avoid waffle and ensure every word delivers value.
Anticipate and answer users’ follow-up questions.
❌ Bad example | ✅ Good example |
Video game crashThe video game crash was kind of a big deal, and it happened for several reasons. Like, there were lots of games and consoles. People didn’t really know what to buy, so they got confused and maybe bored. Sales dropped, and everything just slowed down. It wasn’t great, but eventually things got better somehow. | What caused the video game crash of 1983?Oversaturation, poor-quality games, and lost consumer trust triggered the North American video game crash. Atari flooded the market with underwhelming titles like E.T., while home computers offered better value. Sales plummeted nearly 97%. |
Uses clean, scannable formatting
Generative engines don’t “read” content the way humans do. They scan for structure, identify patterns, and extract meaning.
That means your formatting isn’t just for readability, it’s a core part of how AI models understand and reuse your content. In other words, if your content is easy to scan, it’s easier to surface.
Optimizing content so it is scannable for AI involves the same techniques as making it scannable for humans:
Use short paragraphs of no more than 2 to 4 lines.
Break up your content with descriptive H2 and H3 subheadings.
Use bulleted and numbered lists (these are often lifted directly for AI responses)
Use tables to compare products, data, and strategies.
Demonstrates depth and topical coverage
If you want your content to show up in AI-generated answers, it needs to be the best, most complete resource on the topic.
That means covering not just the main question, but the related questions, follow-ups, and context that users (and AI tools) expect to see.
Pages that go deep and answer a range of connected queries are more useful to generative engines because they can serve multiple parts of an answer, not just one.
It can also be useful to create content clusters using pillar pages and blog posts connected by internal links. This makes it easier for AI models to find the additional depth they need.
Reflect search intent and the user journey
One of the reasons people prefer generative AI search is that it assesses user intent to a deeper extent than standard search. Therefore, you should tailor your content to that intent.
For example, if someone searches for “how does link building work?” you might offer a short explanation followed by a detailed breakdown of methods.
However, if they type “Best link building tools” you could provide a clear, structured comparison of the software available.
Anticipating follow-up questions will also ensure your content covers the subject in detail. For example, if someone searches for tools as mentioned above, then you might include details of costs, user ratings, and where to buy them.
3. Ensure your content screams relevance
While search engines understand content by matching keywords, AI platforms go deeper and seek to understand your content’s meaning.
Signalling relevance to LLMs is a fine balance. You’ll need to focus specifically on the user’s question while also answering the topic in depth.
Here are the factors you need to consider to ensure AI platforms understand your content’s relevance:
Topical alignment
Your content should address the query and cover the topic in depth. For example, if your page is about meal planning for people with diabetes, but it barely covers carb counting or blood sugar management, generative engines may overlook it in favor of a page that directly addresses those key concerns.
Semantic clarity
Use language that aligns with how people talk and search. AI models are trained to understand nuance, synonyms, and user intent, so stuffing exact-match terms isn’t necessary.
Instead, use plain, natural language and structure your content to answer common questions.
For example, a vague or overly technical sentence like:
“Borrowers may be eligible for relief under various fiscal remediation programs.”
Is less likely to be surfaced by AI than:
“If you work in a public service job, you may qualify to have your federal student loans forgiven after 10 years of payments.”
Avoid topic drift
Keep your content tightly focused. Let’s say you’re writing an article about how to prepare for a job interview. If you start discussing how to produce a CV or negotiating your salary halfway through, then LLMs will likely ignore your page in favor of a more focused article.
That’s not to say those topics aren’t useful and relevant. But they belong in separate articles.
4. Use backlinks to signal topical authority and credibility
Backlinks are a cornerstone of SEO. A backlink is simply a link from another website to yours that someone has published because they think your content adds value to them.
Google uses this as a quality signal; if a page gets links from lots of websites, then it assumes the content is trustworthy, authoritative, and worth ranking.
Unlike traditional search engines, AI models like ChatGPT or Perplexity don’t assess ranking factors like backlinks. However, they do pull their answers from high-quality content that ranks on search engines. This means the higher you rank, the more likely you are to be surfaced in AI responses.
And backlinks play a significant role in your site’s ranking. This is highlighted by the fact that the top result for any given Google query has, on average, 3.8x more backlinks than results 2 to 10.
Furthermore, LLMs like to show users information from reputable sources. If your website has lots of backlinks from a range of trusted websites, then it is likely to rank higher and have higher visibility.
AI models take this visibility as a sign that your content is credible. Put simply, backlinks still matter for AI, but not directly.
How GEO linkbuilding is different
Linkbuilders can optimize strategies to ensure content appears in AI responses by building backlinks to the type of content that LLMs use in their response.
As mentioned above, people often use LLMs to quickly summarize informational content. Building links to content like blog posts, guides, statistics, and case studies will help this content appear in these searches.
This impacts the sorts of links you can build. For example, it wouldn’t make sense to build a directory link to a how-to guide.
Instead, you’d focus on techniques that result in editorial, contextually relevant links. Examples include:
Digital PR links
This involves pitching stories to journalists who might link back to your informational content. Search engines consider media organisations trustworthy, and backlinks from these websites are among the most effective.
The easiest way to build these links is using platforms where journalists request expert quotes, like Qwoted or HARO.
Sign up for these platforms and you’ll be able to see questions from journalists. Answer the question well, and you could be quoted in their article and given a backlink.
Here’s a good example: An article on generational definitions in Good Housekeeping quotes a report from the consulting firm McKinsey.

💡Read how to get high-quality PR backlinks to learn more.
Guest posts
When you write guest posts for relevant blogs or publications, you can naturally link back to your own guides or resources as supporting material.
For example, this guest post, where a writer explains the difference between a content creator and an influencer, links to their article listing the best AI story generators.
💡 Read our expert guide to learn more about building guest post backlinks.

If someone is looking for an AI story generator using LLM to search, this link makes it more likely that the round-up will surface.
Resource page links
Many websites maintain curated “resources” or “tools” pages that list helpful guides or reference materials. Earning a link with one of these web pages helps position your content as a go-to
source on the topic, especially if it’s evergreen and answers common questions. Read our guide on building resource page links to learn more.
💬 Need help building authority?
At Linkbuilder, we help you earn high-quality backlinks that boost traditional search engine optimization rankings and improve your chances of being referenced in AI-generated answers.
Whether you're targeting competitive commercial keywords or building informational content hubs, we can help you establish the authority that generative engines seek.
Get in touch to learn more.
5. Technical SEO still underpins everything
Having a strong technical foundation still matters for appearing in search. Like search engines, LLMs want to ensure a good user experience and need clear, well-structured content to understand what your pages are about.
Here’s a reminder of what good technical SEO looks like:
Crawlability and indexing: If your pages aren’t getting crawled or indexed, then AI platforms can’t see them, and they won’t get surfaced in their responses.
Site speed and performance: People hate slow-loading content, and so does AI. Fast-loading sites are easier to parse, more user-friendly, and enable them to provide answers quickly, all of which matters to AI models.
Clean internal linking: Logical, contextual links between your pages help AI models grasp how your content fits together. It also signals topical authority.
HTTPS and site security: Pages served over HTTP (instead of HTTPS) can be flagged as not secure by browsers and search engines, reducing their visibility in traditional search results. This means they will be less likely to appear in AI-generated content.
Focus on showing EEAT
If you’ve worked in SEO for more than five minutes, you’ve heard of E-E-A-T. Originally a Google Search Quality Rater concept, it’s now baked into how content is assessed across both traditional and generative search.
To remind you, it stands for:
Expertise: You can prove you’re an expert in your field, for example, by displaying industry accreditations.
Experience: You have hands-on experience with the topic at hand.
Authority: Others online link to your content because they think their readers will find it valuable.
Trust: You are a legitimate business, run by real people who value user security.
AI models are trained to favour content that looks credible and is written by people who know what they’re talking about.
This makes sense when you think about it. Rather than showing users a list of potential sources and allowing them to find the answer, the AI tells you definitively what the answer is.
This means it’s more important to provide correct information based on trusted sources. Here’s how to build strong E-E-A-T signals:
Add author names, photos, bios, and credentials to your site.
Demonstrate experience by including first-hand insights, examples, or original commentary.
Use external sources, stats, and citations to support your content, and link to credible sites.
Review and refresh key pages regularly. Add a “last updated” date to show your content is maintained.
Use HTTPS to ensure your site is secure.
6. Use schema to make your content machine-readable
Schema markup is code tags that help search engines understand your content by explaining its structure and purpose. It tells them information like:
What questions you’re answering
Who’s behind the content
Whether it’s instructional, informative, or transactional
While LLMs like ChatGPT don’t rely heavily on schema, adding structured data still improves how your content is interpreted, indexed, and surfaced across search and generative platforms.
Useful schema to add to your site include:
FAQPage and HowTo schemas for instructional content
FAQ pages and “how-to” content are often lifted from websites and used in featured snippets and AI-generated summaries. Using these schemas makes it more likely that your content will appear in these prominent positions.
Article or BlogPosting schemas for editorial content
This helps highlight the author, publish date, and article structure, which is useful context for generative tools trying to evaluate freshness and credibility.
Person and Organization schemas for associations
This clearly shows who created the content. This helps search engines and AI systems associate your page with real people and trusted brands, improving credibility and context.
Review, Product, or Event for commercial content
You can use these to make key information like prices, availability, ratings, and event dates easy to extract and display in search or AI-generated summaries.
GEO Is Here: Are You Ready?
Generative Engine Optimization isn’t replacing SEO, it’s evolving it. While traditional search tactics still matter, there’s now more to consider. If your content can’t be understood, cited, or trusted by AI, it may never be surfaced, significantly reducing your visibility.
That’s why many SEOs no longer just want to rank on page one. They also aim to become the source that AI pulls from when users ask questions.
From earning high-authority backlinks to structuring your content for AI readability, GEO is about building credibility and clarity online.
Want help building AI-friendly authority?
At Linkbuilder, we specialise in helping businesses earn links to the type of content that generative engines and users trust.
Whether you're building topical hubs, targeting competitive keywords, or simply trying to stay visible as search evolves, we’re here to help. Get in touch and let’s talk strategy.

